-
Whatsapp: +86 13526572721
-
Email: info@zydiamondtools.com
-
Address: AUX Industrial Park, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
-
Whatsapp: +86 13526572721
-
Email: info@zydiamondtools.com
-
Address: AUX Industrial Park, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
How to Choose the Right Grinding Wheel for Camshaft Machining?

So, with all the options available, how do you actually choose the perfect grinding wheel for machining a camshaft?
Choosing the right grinding wheel for camshaft machining requires a systematic approach focusing on three critical areas: selecting the correct abrasive material for your camshaft, matching the wheel’s technical specifications to your quality requirements, and ensuring complete compatibility with your grinding machine.
This involves deciding between CBN and Ceramic Alumina abrasives, defining key specifications like wheel dimensions, grit size, and bond type, and verifying machine compatibility by checking brand matchups, RPM safety ratings, and the arbor hole size. Getting these elements right is the key to achieving precision, efficiency, and operational safety.
Selecting the Optimal Abrasive Material
When it comes to grinding camshafts, the choice of abrasive material is one of the most important decisions you will make.
The best abrasive for camshaft grinding depends primarily on two factors: the material of the camshaft itself (like hardened steel or cast iron) and your production volume. For high-volume production and grinding hard materials, Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is the superior choice due to its long life and precision.
For lower-volume jobs or grinding softer materials like cast iron, Ceramic Alumina offers a highly effective and more cost-efficient solution. Choosing correctly involves balancing the initial wheel cost against long-term performance, cycle times, and the specific quality demands of the final product.
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) Wheels: For High-Performance and Precision
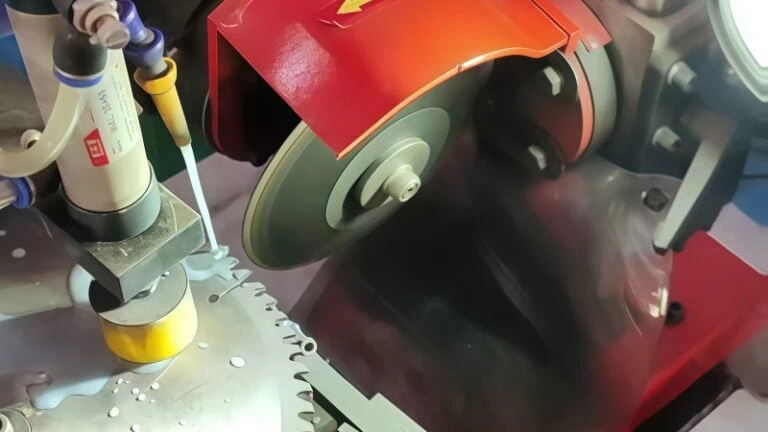
Cubic Boron Nitride, or CBN, is a synthetic abrasive that is second only to diamond in hardness. Because it is so hard and resistant to heat, it is the premier choice for grinding hardened materials under the demanding conditions of high-volume manufacturing.
Superior Hardness and Thermal Stability
The main advantage of CBN is its ability to grind hardened steel camshafts (typically those with a hardness of 55 HRC or higher) without creating excessive heat. In grinding, heat is the enemy. Too much heat can cause thermal damage, creating microscopic cracks or soft spots on the camshaft lobe surface, which leads to premature engine failure.
CBN’s high thermal stability means it transfers most of the heat away with the metal chips, keeping the camshaft surface cool and undamaged. This results in a higher quality, more reliable part with a consistent surface finish, which is critical for modern engine performance.
Exceptional Form Holding and Longevity
Have you ever wondered how a manufacturer can produce thousands of identical camshafts? The answer often lies in CBN’s incredible form-holding capability. This means the wheel keeps its precise shape for a very long time.
- Consistency: Because the wheel doesn’t wear down quickly, every camshaft it grinds has the same precise lobe profile. This is essential for ensuring consistent engine timing and performance.
- Reduced Downtime: A single vitrified CBN wheel1 can often grind over 100,000 camshaft lobes before it needs to be “dressed” (reshaped)2. In contrast, a conventional wheel might need dressing after only a few hundred. This drastic reduction in downtime for wheel maintenance is a massive productivity gain in an automotive production line.
Ceramic Alumina Wheels: A Cost-Effective Alternative
Ceramic Alumina is not your standard abrasive. It is an advanced, synthetically produced grain that is tougher and sharper than conventional aluminum oxide. Its key feature is its micro-crystalline structure; as the grain wears, old, dull micro-crystals break away, exposing new, sharp cutting edges. This self-sharpening action keeps the wheel cutting efficiently for longer.
Excellent Performance on Softer Metals
While CBN excels on hardened steel, Ceramic Alumina is an outstanding performer on softer materials, most notably chilled cast iron. Many camshafts, especially in the aftermarket and for certain types of industrial engines, are made from cast iron. Ceramic Alumina wheels provide a fantastic balance of a fast cutting rate and a fine surface finish on these materials, all at a lower initial cost than CBN.
When to Choose Ceramic Alumina
Choosing a Ceramic Alumina wheel makes perfect sense in several scenarios:
- Job Shops and Engine Rebuilders: When you are grinding a variety of different camshafts in small batches, the high upfront investment of a CBN wheel may not be justifiable.
- Budget-Conscious Operations: It provides professional-grade results without the premium price tag of CBN.
- Cast Iron Applications: It is often the technically preferred abrasive for chilled cast iron, delivering optimal performance without being overly aggressive.
Matching Abrasive to Camshaft Material (Cast Iron vs. Forged Steel)
Ultimately, your choice comes down to matching the tool to the job. Using the wrong abrasive is like trying to cut a steak with a butter knife—it’s inefficient and produces poor results. The table below provides a clear guide for making this critical decision.
| Camshaft Material | Recommended Abrasive | Key Reason | Ideal Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardened Forged Steel (>55 HRC) | CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) | Unmatched hardness and thermal stability are required to cut without damaging the workpiece. | High-volume automotive OEM, performance engine manufacturing. |
| Chilled or Ductile Cast Iron | Ceramic Alumina | Excellent cutting action and surface finish on iron at a lower cost; self-sharpening for good wheel life. | Aftermarket parts, engine rebuilding, lower-volume production. |
This choice is a foundational one. The specific grade and composition of a CBN or Ceramic Alumina wheel can also be fine-tuned for optimal performance. Consulting with your supplier is the best way to match a specific wheel grade to your material’s hardness and your production goals.
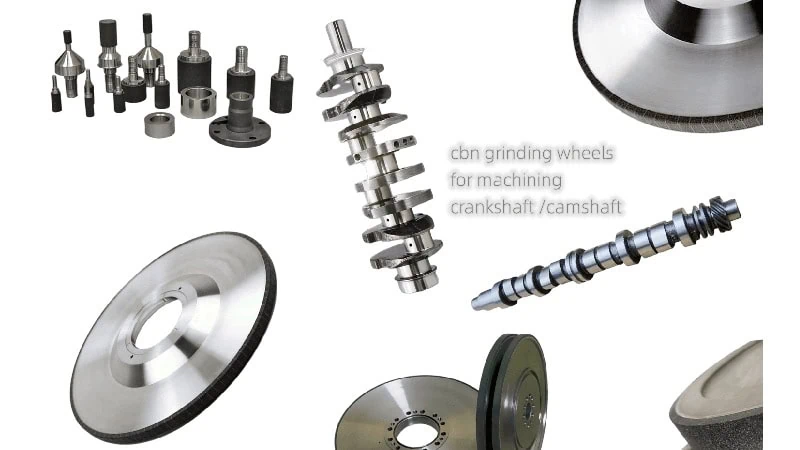

Understanding Key Wheel Specifications
Beyond the abrasive material, certain technical specifications of the wheel will have a major impact on your grinding results.
To select the right grinding wheel, you must focus on three key specifications: the wheel’s dimensions (diameter and thickness) to fit your machine, the abrasive grit size to control the material removal rate and final surface finish, and the bond type3 that holds the abrasives together.
Getting these three specifications right is essential for efficient, high-quality camshaft grinding. The dimensions ensure physical compatibility, the grit size determines the speed and quality of the cut, and the bond type dictates the wheel’s performance and lifespan under specific operating conditions.
Selecting the Correct Wheel Diameter and Thickness
First and foremost, a grinding wheel must physically fit your machine. This is a critical first step. Think of it like buying tires for a car; you can’t use a truck tire on a small sedan, no matter how good the tire is.
The diameter of the wheel is crucial because it determines the surface speed at which the abrasive grains contact the camshaft. Grinding machines are designed for a specific range of wheel diameters to achieve the optimal surface feet per minute (SFM), a key parameter for effective grinding. Using a wheel that is too large or too small can lead to poor surface finish or safety hazards. For instance, many CNC camshaft grinders, such as those from Landis or Schaudt, are engineered for wheels in the range of 400mm to 600mm (approximately 16 to 24 inches) in diameter.
The thickness of the wheel must match the width of the camshaft lobe or journal you are grinding. If the wheel is too narrow, you will need to make multiple passes, which is inefficient. If it’s too wide, you risk grinding adjacent features. The wheel thickness must be chosen to provide adequate clearance while maximizing contact for efficient grinding.
Understanding Grit Size for Roughing vs. Finishing
Grit size refers to the size of the individual abrasive particles in the wheel. It is measured on a scale where a lower number means larger, more aggressive grains, and a higher number means smaller, finer grains. Choosing the right grit size is a trade-off between speed and finish.
- Rough Grinding (Roughing): This is the first stage, where the primary goal is to remove a large amount of material quickly. For this, you would use a wheel with a lower grit number (e.g., 60 to 80 grit). The large abrasive grains act like powerful chisels, rapidly shaping the camshaft lobe, but leave a rougher surface.
- Finish Grinding (Finishing): After roughing, the goal is to produce a smooth, precise final surface. This requires a wheel with a higher grit number (e.g., 120 to 180 grit or even higher for CBN wheels). The small, fine grains take very small chips, polishing the surface to its final dimension and finish.
In many modern production environments, a single CBN wheel might be used with different grinding parameters to achieve both roughing and finishing cycles. However, the principle remains the same. Here is a simple breakdown:
| Grinding Stage | Goal | Typical Grit Size Range | Resulting Surface |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roughing | Fast material removal | 60 – 80 | Coarse, dull |
| Finishing | Smooth final surface | 120 – 180+ | Fine, reflective |
The ideal grit size can depend on the abrasive type and the specific surface finish (Ra)4 required by the part’s blueprint. Since these values can be adjusted for specific applications, it’s wise to refer to your supplier’s recommendations to select the grit that best balances cycle time and finish requirements.
The Role of Bond Type in Grinding Performance
The bond is the glue that holds the abrasive grains in place. It plays a huge role in how the wheel performs. For camshaft grinding, the most common and effective bond is the vitrified bond.
Vitrified Bonds: The Industry Standard
Vitrified bonds are essentially a type of glass fired at high temperatures to create a strong, rigid, and porous structure around the abrasive grains.
- Strength and Rigidity: The rigid nature of a vitrified bond5 ensures the wheel holds its precise shape, which is absolutely essential for maintaining the tight tolerances of a camshaft profile.
- Porosity: The pores, or empty spaces, within the bond structure are critical. They provide clearance for the tiny metal chips cut from the camshaft, preventing the wheel from “loading up” or clogging. They also allow grinding fluid (coolant) to reach the cutting zone, which dissipates heat and improves the surface finish.
- Aggressive Cutting: Vitrified bonds allow for high material removal rates while holding form, making them perfect for the demands of production grinding.
While other bond types like resin or metal exist, they are less common in high-precision camshaft grinding. The combination of a high-performance abrasive like CBN with a strong, porous vitrified bond is the formula that top-tier automotive and engine manufacturers rely on to produce high-quality camshafts.
Ensuring Machine and Wheel Compatibility
After choosing the right material and specifications, you must be certain that the grinding wheel will work perfectly and safely with your specific machine.
To ensure compatibility, you must first confirm that the wheel is designed for your specific brand of CNC grinder. Next, you must verify that the machine’s operating RPM is safely below the maximum RPM rating of the wheel. Finally, you must ensure the wheel’s arbor hole precisely matches the machine’s spindle.
These three checks are non-negotiable for safe and effective operation. Matching the wheel to the machine brand ensures it meets performance standards. Adhering to RPM ratings prevents catastrophic wheel failure. A correct arbor hole size guarantees a secure, balanced fit, which is essential for precision grinding.
Matching Wheels to Major CNC Grinder Brands (Landis, Toyoda, Junker)
High-performance CNC grinding machines are complex, finely-tuned systems. Leading manufacturers like Landis, Toyoda, and Junker design their machines with specific performance characteristics in mind. Consequently, premier grinding wheel manufacturers engineer wheels to complement these systems.
Choosing a wheel specified as “suitable for Landis LT2” or “compatible with Toyoda GL-series grinders” indicates that the wheel has been designed and tested to:
- Handle the machine’s specific power and torque output.
- Work effectively with the machine’s coolant delivery system.
- Meet the balancing requirements needed for high-speed, vibration-free operation.
Choosing a wheel that is explicitly matched to your machine brand is the first step in guaranteeing a seamless integration and predictable, high-quality results.
Verifying RPM Ratings and Safety Standards
This is arguably the most important safety check you will perform. Every grinding wheel has a maximum safe operating speed, measured in Revolutions Per Minute (RPM), which is printed directly on the wheel’s label. This RPM rating is the absolute top speed at which the wheel can spin before the centrifugal force6 threatens to tear it apart.
It is critical that the maximum operating RPM of your grinding machine’s spindle never exceeds the RPM rating of the wheel.
For example, if your machine’s spindle is capable of running at 3,500 RPM, you must never mount a wheel with a maximum rating of only 3,000 RPM. Operating a wheel above its rated speed is one of the leading causes of catastrophic wheel failures, which can result in serious injury and machine damage.
Safety First: Always check the RPM rating on the wheel and compare it to your machine’s settings before mounting. If the wheel’s maximum RPM is not listed or is illegible, do not use the wheel. There is no compromise when it comes to safety.
Reputable wheel manufacturers test their products rigorously to ensure they meet strict safety standards.
The Importance of Arbor Hole Size
The arbor hole is the hole in the center of the grinding wheel that mounts onto the machine’s spindle. The fit between the arbor hole and the spindle must be exact.
- If the hole is too small, it simply won’t fit on the spindle.
- If the hole is too large, the wheel will be off-center and severely out of balance. When spun at thousands of RPM, this imbalance will cause massive vibrations, making it impossible to grind a precise surface and creating a significant risk of failure.
Imagine trying to spin a bicycle wheel that isn’t attached correctly at its center axle—it would wobble uncontrollably. The same principle applies here, but at much higher speeds and with much more serious consequences.
The arbor hole size is a standard dimension and must be an exact match to your machine. For example, many large-diameter camshaft grinding wheels use a standard arbor hole size like 203.2mm (8 inches) or 304.8mm (12 inches). Because these dimensions are standardized yet vary between machine models, it is essential to confirm the exact arbor hole diameter required by your machine from its technical manual before ordering a wheel.
Conclusion
Selecting the ideal grinding wheel is not about finding a single “best” product, but about conducting a thorough analysis of your specific needs. By systematically evaluating the camshaft material, defining the right wheel specifications, and confirming absolute compatibility with your machine, you move from guesswork to a precise engineering decision. A well-chosen grinding wheel is more than just a consumable part; it is a critical investment in the quality of your finished product, the efficiency of your operation, and the safety of your workplace.
References
- vitrified CBN wheel1 – The product page for ZYDiamondTools’ CBN Grinding Wheels specifically designed for camshaft machining.
- “dressed” (reshaped)2 – A practical how-to guide on the process and importance of dressing diamond and CBN grinding wheels, from ZYDiamondTools.
- bond type3 – A ZYDiamondTools guide explaining the different types of grinding wheel bonds and how to select the right one.
- surface finish (Ra)4 – An engineering guide from Get It Made that explains the concepts and measurement of surface roughness.
- vitrified bond5 – A comprehensive guide from ZYDiamondTools on the selection and use of vitrified bond diamond and CBN grinding wheels.
- centrifugal force6 – A Wikipedia article providing a detailed explanation of centrifugal force, its physics, and applications.